- +(94) 71 196 7228
- info@seclk.com
- Mon - Fri 8:00 - 17:30
- August 26, 2023
- by SE Consultants
Timber Stud Wall Framing: The Backbone of Structural Integrity
Timber Stud Wall Framing: The Backbone of Structural Integrity
The objectives of wall system design
- to resist snow, live, and dead loads and wind and seismic forces;
- to provide an adequate subsurface for wall finishes and to provide openings for doors and windows;
- to serve as a thermal and weather barrier;
- to provide space and access for electrical and mechanical equipment, where required
- to provide a one- two-hour fire barrier if the wall separates individual dwelling units in attached or multifamily buildings.
Introduction
A wall serves as a vertical structural system responsible for carrying the weight of the roof and floors above, transmitting these loads to the foundation below. It plays a crucial role in resisting lateral forces caused by wind and earthquakes. The typical composition of a wood-framed wall includes various elements, such as studs (including wall, cripple, jack, and king studs), top and bottom plates, headers, sheathing, and optional diagonal let-in braces. While traditional residential wall systems have been constructed using dimension lumber, like 2x4s or 2x6s, there is a growing trend in the use of engineered wood studs and cold-formed steel studs.
Wall studs are vertical framing members spaced at regular intervals to support the wall sheathing. They extend the entire height of each story and bear the load from the floors above. King and jack studs, also known as jamb studs, are used to frame openings and provide support for loads transferred by a header. On the other hand, cripple studs are not full height and are positioned above or below a wall opening. Additionally, built-up wall studs, assembled on-site, may be used to support concentrated loads within the wall. The top and bottom plates are horizontal members to which the studs are attached. These plates are fastened to the floor or roof above and either to the floor below or directly to the foundation.
Headers, functioning as beams, effectively transfer the loads from an opening to jack studs located on each side of the opening. This ensures proper load distribution and structural integrity around the opening area.
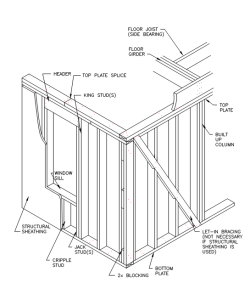
Figure 1- Structural elements of a Wall system.
Understanding Timber Stud Wall Framing
Timber stud wall framing involves assembling a framework of vertical wooden members (studs) that are spaced apart to create wall structures. These studs serve as load-bearing elements, supporting the weight of the roof and upper floors, while also providing stability and shape to the building. Horizontal top and bottom plates secure the studs in place, and additional components, such as headers and sills, are integrated to accommodate doors and windows.
Benefits of Timber Stud Wall Framing
- Strength and Durability: Timber stud walls are renowned for their strength and resilience, making them capable of withstanding various loads and stresses over extended periods. Properly constructed timber stud walls have excellent load-bearing capacities, contributing to the overall structural integrity of the building.
- Design Flexibility: The adaptability of timber stud wall framing allows architects and builders to design spaces with flexibility. Walls can be easily modified or reconfigured, accommodating changes in floor plans or future expansions.
- Thermal and Acoustic Insulation: Timber is a natural insulator, providing effective thermal and acoustic properties that contribute to energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Timber stud walls can significantly reduce heat transfer and noise transmission, creating a more pleasant and sustainable indoor environment.
- Sustainable and Eco-Friendly: Timber is a renewable resource, making timber stud wall framing a sustainable choice for environmentally conscious construction. Using wood in building projects also contributes to carbon sequestration, reducing the overall carbon footprint of the structure.
Construction Process
The construction of timber stud walls follows a systematic process:
- Layout and Marking: Builders mark the positions of the wall plates and studs on the foundation and adjacent walls, ensuring accuracy in measurements.
- Assembly: The studs are cut to the desired height and placed vertically between the top and bottom plates. Careful spacing between studs allows for the insertion of insulation and electrical wiring.
- Fastening: Nails or screws are used to secure the studs to the plates, creating a stable frame.
- Adding Headers and Sills: Headers are placed above doors and windows to distribute the load, while sills are installed beneath them for support.
Fire and Termite Resistance
Timber stud wall framing can be treated to improve fire resistance, reducing the risk of rapid fire spread and enhancing overall safety. Additionally, proper treatment and moisture barriers can protect the wood from termite infestations, extending the life of the structure.
Conclusion
Timber stud wall framing is a time-honored construction method that combines strength, durability, and environmental sustainability. From residential homes to commercial buildings, this versatile technique offers design flexibility, excellent insulation, and structural integrity. Embracing timber stud wall framing not only ensures a reliable and efficient structure but also contributes to a greener and more sustainable construction industry. Whether in new builds or renovation projects, timber stud walls remain a cornerstone of modern construction practices.

